
Bangladesh has commenced the issuance of e-passports to its citizens. I believe you may find it intriguing to understand the meaning of an e-passport and the disparities between a Machine Readable Passport (MRP) and an E-Passport. So, what exactly is an E-Passport? As per the information provided by the Department of Immigration and Passport, an e-passport refers to a biometric passport equipped with an electronic chip.
Bangladesh has initiated the issuance of e-passports to its citizens. It may pique your curiosity to learn about the concept of an e-passport and understand the distinctions between a machine-readable passport (MRP) and an E-Passport.
What is an E-Passport?
The e-passport, as stated by the Department of Immigration and Passport, is a passport equipped with an electronic chip that stores biometric information. This information is utilized for verifying the identity of the passport holder.
The e-passport utilizes a microprocessor along with chips and antennas. Crucial passport details are stored on the chip. This e-passport captures biometric information such as photos, fingerprints, and Eyeris. The electronic border control system (E-Border) then compares the biometric data from the passport chip with external validation
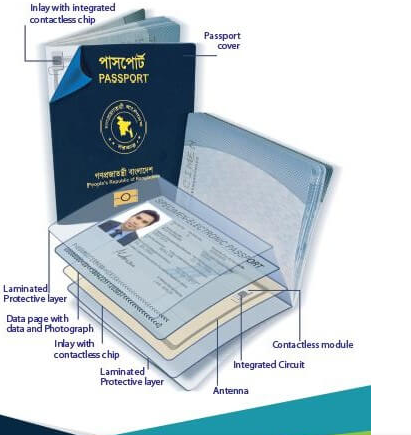
Fraud is difficult to commit as the information stored on the passport chip undergoes verification using Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
Difference between E-Passport and Normal Passport
The primary distinction between a regular Machine Readable Passport (MRP) and an e-passport is:
An average passport includes a machine-readable zone (MRZ) printed according to the guidelines of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
In contrast, an ePassport has a built-in IC chip that stores all the bearer’s biometric information, including their photograph and personal details, following ICAO specifications.
An average passport includes a machine-readable zone (MRZ) printed according to the guidelines of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
The e-passport is equipped with a compact and slender chip, similar to the SIM card of a mobile phone. This chip contains numerous concealed features and securely stores all the necessary security information. When obtaining an e-passport, the data from the machine-readable passport (MRP) database will be transferred to the e-passport.
To apply for an e-passport, it is mandatory to submit an online application, eliminating the need for a physical or PDF application form. In contrast, for an MRP passport, an applicant may choose to fill out a PDF form manually, if preferred.
To obtain an e-passport, it is necessary to possess a National ID Card. Without a national ID card, one cannot apply for an e-passport.
However, a MRP passport can be obtained with a Birth Registration Certificate.
During the application process, the applicant will be required to provide a photograph, 10 fingerprints, and their Eyeris scan. These details will be stored on the passport’s chip. The immigration police will have access to all this information by scanning the passport page on a specialized machine.
There are two types of e-passports available, one with 48 pages and another with 64 pages. The fees for obtaining an e-passport vary depending on the type of service required, such as general, emergency, or urgent. Please refer to the e-passport fee schedule for more information.



